WORLD IS DEPENDED ON INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY, INFORMATION CAN'T STOP THEY ALWAYS PROCESS AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY DEPEND ON SOFTWARE ENGINEER WORK HARD BUT LOGICALLY
Thursday, 5 December 2013
C++ Program to create a loading flash
#include<iostream>
#include<unistd.h>
using namespace std;
main()
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<=100;i++)
{
cout<<"Loading......."<<i<<"%\r";
usleep(100000);
}
return 0;
}
COMPUTER TRICKS:
Interesting Facts About C Programming
Language ..............
Firstly When C Was Introduced Then There Was Already
Seven Life Cycle Evoked
Following By .............
1 : ALGOL Stands For Algorithm Programming System
Introduced In 1960 And Was The First To Use Block
Structure
Computer Scientist : Bohm , Jacopini And Edsger
2 : BCPL (Basic Combined Programming Language) Was
Introduced In 1967 By Richard
3 : B.B Was Later Used To Create Version Of UNIX At Bell
Lab ........
Language ..............
Firstly When C Was Introduced Then There Was Already
Seven Life Cycle Evoked
Following By .............
1 : ALGOL Stands For Algorithm Programming System
Introduced In 1960 And Was The First To Use Block
Structure
Computer Scientist : Bohm , Jacopini And Edsger
2 : BCPL (Basic Combined Programming Language) Was
Introduced In 1967 By Richard
3 : B.B Was Later Used To Create Version Of UNIX At Bell
Lab ........
COMPUTER TRICKS:
Interesting Facts About C Programming
Language ..............
Firstly When C Was Introduced Then There Was Already
Seven Life Cycle Evoked
Following By .............
1 : ALGOL Stands For Algorithm Programming System
Introduced In 1960 And Was The First To Use Block
Structure
Computer Scientist : Bohm , Jacopini And Edsger
2 : BCPL (Basic Combined Programming Language) Was
Introduced In 1967 By Richard
3 : B.B Was Later Used To Create Version Of UNIX At
Bell
Lab ........
Ruby for Beginners V3
Lesson 1: Introduction
Welcome to the LearnStreet beginner course
on Ruby. In this course, you'll learn how to code in Ruby, a flexible
yet powerful programming language that’s popular over the web. Some of
the most popular websites--like Twitter, Groupon, and Hulu--are built on
top of Ruby on Rails (also known as RoR or Rails), a web application
framework for the Ruby programming language. If you'd like to learn more about setting up Ruby on your own PC or Mac, please click here. This step is not required for the course, but it will help you test and practice some concepts as you go along.
This course is designed for people who have no prior programming knowledge, so we'll teach you fundamental programming concepts as we go. Throughout the course, you'll write code to apply what you've learned to solve programming problems. In addition, after you complete the course, you'll code functionality to build a LearnStreet Bank project, which you’ll be able to share with your friends.
Python for Beginners V3
Lesson 1: Introduction to Python
Welcome to the LearnStreet beginner course
on Python. The Python programming language is
a high level programming language that is used in a wide spectrum of
applications -- from web design and game programming to scientific
research. Its simple and flexible syntax makes it easy to learn and
understand, but still powerful and expressive. By the end of this
course, you'll have a solid understanding of the Python language, and be
able to complete some cool projects in the Code Garage section. Keep
in mind this course uses Python version 2.7. Python 2.7 is more widely
used in industry, and therefore more valuable to learn. The most recent
version is 3.2, which has some key syntax differences.We have designed this course for people who have no prior programming background. In this course, we will teach you some fundamental programming concepts through Python. Throughout this course, you will write code to apply what you've learned to solve programming problems.
Now, click on the big black box - the Python interpreter - below this to start coding away!
Beginner JavaScript Course V3
Argument
A variable that represents a value passed into a function or method.Arithmetic Operator
One of several operators that perform arithmetic between variables or values. They include; +, -, *, /, %, ++, --Array
An Object that represents a list of elements that are accessed by their position within the list. An Array also has built in properties and methods.Assignment
Assigning a value to a variable or property.Assignment Operator
One of several operators that assign a value to a variable. They include; =, +=, -=, *=, /=, %=Booleans
Syntax
true false
Example
expression1 && expression2 expression3 || expression4 !expression5
Break
A statement that will cause immediate exit from a loop once it is encountered and normal flow of execution will continue with the statement immediately following the loop.Case
Used in conjunction with a Switch statement, the "case" statement identifies a value for a conditional test against the switch parameter. When the switch parameter and case value are equal, the code following the case statement is executed.Code Block
A grouped collection of statements that are meant to be executed together and most often denoted by surrounding curly braces.Code comments
A comment is generally used within code to explain how something works or to write necessary information about a section. Comments are very useful to make code more readableSyntax
Single Line Comment // Comment comment comment Multi-Line Comment /*Comment1 Comment2 . . Comment3 */
Comparison Operator
One of several operators that determine the equality of two variables or values. They include; ==, ===, !-, !===, >, >=, <, <=Conditional Test
A test for true or false, that is; testing for a certain condition.Constant
A fixed value such as "this is constant" or the number 10.Construct
An idea or theory construction of operators, keywords and variables.Continue
When a "continue" statement is encountered in a loop, all remaining statements in the current loop iteration are skipped but looping will continue.Do...While
A flow control mechanism that can be explained as:Argument
A variable that represents a value passed into a function or method.Arithmetic Operator
One of several operators that perform arithmetic between variables or values. They include; +, -, *, /, %, ++, --Array
An Object that represents a list of elements that are accessed by their position within the list. An Array also has built in properties and methods.Assignment
Assigning a value to a variable or property.Assignment Operator
One of several operators that assign a value to a variable. They include; =, +=, -=, *=, /=, %=Booleans
Syntax
true false
Example
expression1 && expression2 expression3 || expression4 !expression5
Break
A statement that will cause immediate exit from a loop once it is encountered and normal flow of execution will continue with the statement immediately following the loop.Case
Used in conjunction with a Switch statement, the "case" statement identifies a value for a conditional test against the switch parameter. When the switch parameter and case value are equal, the code following the case statement is executed.Code Block
A grouped collection of statements that are meant to be executed together and most often denoted by surrounding curly braces.Code comments
A comment is generally used within code to explain how something works or to write necessary information about a section. Comments are very useful to make code more readable.Syntax
Single Line Comment // Comment comment comment Multi-Line Comment /*Comment1 Comment2 . . Comment3 */
Comparison Operator
One of several operators that determine the equality of two variables or values. They include; ==, ===, !-, !===, >, >=, <, <=Conditional Test
A test for true or false, that is; testing for a certain condition.Constant
A fixed value such as "this is constant" or the number 10.Construct
An idea or theory construction of operators, keywords and variables.Continue
When a "continue" statement is encountered in a loop, all remaining statements in the current loop iteration are skipped but looping will continue.Do...While
A flow control mechanism that can be explained as:do {something} while(condition is true)
Element
This is a general reference to variables, objects, arrays and individual objects within objects and arrays.Execute
Running a software program, single line of code, function a block of code or any unit of software.Flow Control
The means by which the logic in a software program determines the flow of execution of the code.For
A loop flow control mechanism that can be explained as:for (i=n; condition is true; i++) {do something}
Saturday, 12 October 2013
Partial derivative: CH:5 IN ENGINEERING
In mathematics, a partial derivative of a function of several variables is its derivative with respect to one of those variables, with the others held constant (as opposed to the total derivative, in which all variables are allowed to vary). Partial derivatives are used in vector calculus and differential geometry.
The partial derivative of a function f with respect to the variable x is variously denoted by
Introduction:
Suppose that ƒ is a function of more than one variable. For instance,
The graph of this function defines a surface in Euclidean space. To every point on this surface, there are an infinite number of tangent lines. Partial differentiation is the act of choosing one of these lines and finding its slope. Usually, the lines of most interest are those that are parallel to the xz-plane, and those that are parallel to the yz-plane (which result from holding either y or x constant, respectively.)
To find the slope of the line tangent to the function at P(1, 1, 3) that is parallel to the xz-plane, the y variable is treated as constant. The graph and this plane are shown on the right. On the graph below it, we see the way the function looks on the plane y = 1. By finding the derivative of the equation while assuming that y is a constant, the slope of ƒ at the point (x, y, z) is found to be:
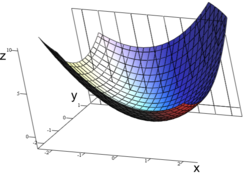

Definition:
Basic definition,
The function f can be reinterpreted as a family of functions of one variable indexed by the other variables:In general, the partial derivative of a function f(x1,...,xn) in the direction xi at the point (a1,...,an) is defined to be:
 , and by definition,
, and by definition,An important example of a function of several variables is the case of a scalar-valued function f(x1,...xn) on a domain in Euclidean space Rn (e.g., on R2 or R3). In this case f has a partial derivative ∂f/∂xj with respect to each variable xj. At the point a, these partial derivatives define the vector
A common abuse of notation is to define the del operator (∇) as follows in three-dimensional Euclidean space R3 with unit vectors
 :
: ):
):Formal definition
Like ordinary derivatives, the partial derivative is defined as a limit. Let U be an open subset of Rn and f : U → R a function. The partial derivative of f at the point a = (a1, ..., an) ∈ U with respect to the i-th variable ai is defined asThe partial derivative
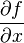 can be seen as another function defined on U
and can again be partially differentiated. If all mixed second order
partial derivatives are continuous at a point (or on a set), f is termed a C2 function at that point (or on that set); in this case, the partial derivatives can be exchanged by Clairaut's theorem:
can be seen as another function defined on U
and can again be partially differentiated. If all mixed second order
partial derivatives are continuous at a point (or on a set), f is termed a C2 function at that point (or on that set); in this case, the partial derivatives can be exchanged by Clairaut's theorem:
Examples:
The volume V of a cone depends on the cone's height h and its radius r according to the formula

By contrast, the total derivative of V with respect to r and h are respectively
If (for some arbitrary reason) the cone's proportions have to stay the same, and the height and radius are in a fixed ratio k,
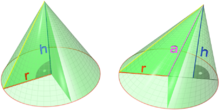
Notation:
For the following examples, let f be a function in x, y and z.First-order partial derivatives:

Antiderivative analogue:
There is a concept for partial derivatives that is analogous to antiderivatives for regular derivatives. Given a partial derivative, it allows for the partial recovery of the original function.
Consider the example of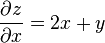 . The "partial" integral can be taken with respect to x (treating y as constant, in a similar manner to partial derivation):
. The "partial" integral can be taken with respect to x (treating y as constant, in a similar manner to partial derivation):

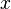 will disappear when taking the partial derivative, and we have to
account for this when we take the antiderivative. The most general way
to represent this is to have the "constant" represent an unknown
function of all the other variables.
will disappear when taking the partial derivative, and we have to
account for this when we take the antiderivative. The most general way
to represent this is to have the "constant" represent an unknown
function of all the other variables.Thus the set of functions
 , where g is any one-argument function, represents the entire set of functions in variables x,y that could have produced the x-partial derivative 2x+y.
, where g is any one-argument function, represents the entire set of functions in variables x,y that could have produced the x-partial derivative 2x+y.If all the partial derivatives of a function are known (for example, with the gradient), then the antiderivatives can be matched via the above process to reconstruct the original function up to a constant
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)

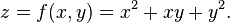
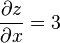







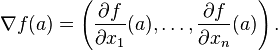
![\nabla = \bigg[{\frac{\partial}{\partial x}} \bigg] \mathbf{\hat{i}} + \bigg[{\frac{\partial}{\partial y}}\bigg] \mathbf{\hat{j}} + \bigg[{\frac{\partial}{\partial z}}\bigg] \mathbf{\hat{k}}](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/f/e/4/fe4954365d1dc12dbbc804b923dfdae3.png)
![\nabla = \sum_{j=1}^n \bigg[{\frac{\partial}{\partial x_j}}\bigg] \mathbf{\hat{e}_j} = \bigg[{\frac{\partial}{\partial x_1}}\bigg] \mathbf{\hat{e}_1} + \bigg[{\frac{\partial}{\partial x_2}}\bigg] \mathbf{\hat{e}_2} + \bigg[{\frac{\partial}{\partial x_3}}\bigg] \mathbf{\hat{e}_3} + \dots + \bigg[{\frac{\partial}{\partial x_n}}\bigg] \mathbf{\hat{e}_n}](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/0/8/b/08b7a94d4e192df78103570d96fcd1c3.png)












